In-depth insights into Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Sofie Geurts
Junior Consultant at NAALA
Published on 24 January, 2024
By: Sofie Geurts – Junior Consultant at NAALA
Published on 24 January, 2024
In this blog post, we will explore the concept of Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) and how you can effectively carry out these assessments to identify and mitigate data protection risks. DPIAs are a crucial step in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and safeguarding individuals’ privacy rights. We will discuss the purpose of DPIAs, their key components, and the steps you need to take when carrying out a DPIA. European guidelines have been published to elaborate on the legislation about DPIAs. These guidelines can be used to help carry out a DPIA.
In a nutshell
- Risk assessment. DPIAs help identify and minimize data protection risks when processing data.
- Penalties. DPIAs are mandatory when processing personal data, which poses a high risk to privacy rights.
- Benefits. Conducting a DPIA ensures compliance, prevents excessive data processing, and addresses potential issues early on.
- Key elements. A DPIA describes processing details, assessing necessity and proportionality, evaluating risks to individuals, and implementing additional measures to mitigate risks.
- Continuous. A DPIA process follows a continuous cycle, with specific stages to be performed. This allows for onoing risk management and adaptation to changing circumstances.
What is a DPIA?
- Understanding DPIAs. A Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) is a process designed to help identify, analyze and minimize the data protection risks of a data processing activity. A DPIA is closely related to the accountability obligations under the GDPR. When done correctly, a DPIA can help demonstrate that an organization complies with requirements such as the accountability principle under the GDPR.
- Data protection risk management. A DPIA helps to minimize risks that may arise from the processing of personal data. In addition, the process helps to determine whether or not the level of risk is acceptable in the circumstances. The process is a tool that can be used across a wide variety of data processing activities and projects.
Is a DPIA mandatory?
- High-risk processing. Performing DPIA is mandatory whenever processing personal data is likely to result in a high risk to the privacy rights of the persons involved. This can be seen in the legal text of the provision in the GDPR below.
- Automated decision-making and profiling. Conducting a DPIA is particularly required when making decisions based on systematic and comprehensive assessments, such as automated processing or profiling, which have legal consequences for individuals. It’s also crucial when special personal data, like health data, is processed on a large scale.
- Listed situations. There are certain processing activities for which a DPIA is always necessary. The Dutch Data Protection Authority provides a list of situations of such situations where conducting a DPIA is mandatory.
- Documentation for compliance. Finally, it’s essential to document the DPIA process and outcomes. This documentation not only serves as evidence that a DPIA was conducted and the rationale behind it but also as proof of compliance with GDPR requirements.
Why is it important?
- Looking ahead. Performing a DPIA before starting data processing is crucial for legal compliance and proactive data protection. It is a preventive measure that helps organizations avoid excessive data processing and subsequent delays. By conducting a DPIA early, organizations can anticipate necessary safeguards, enhancing efficiency and preparedness in managing privacy risks.
- Accountability. The DPIA is integral to fulfilling the accountability obligations of the GDPR. It enables organizations to identify and mitigate privacy risks, integrate data protection into their processes, maintain necessary documentation, and demonstrate their commitment to compliance with GDPR requirements.
- Legal necessity. Under the GDPR, conducting a DPIA is mandatory for processing likely to pose high risks to individual rights and freedoms. Failure to conduct a DPIA when required can result in enforcement actions, such as fines. The DPIA serves as a critical tool for compliance with the GDPR.
- Awareness. Consistently conducting DPIAs enhances an organization’s awareness of privacy and data protection issues. It involves practical steps to identify and mitigate privacy risks, ensuring that data processing is privacy-safe. A DPIA offers broader compliance benefits, effectively assessing and demonstrating adherence to all data protection principles and obligations.
How to perform a DPIA?
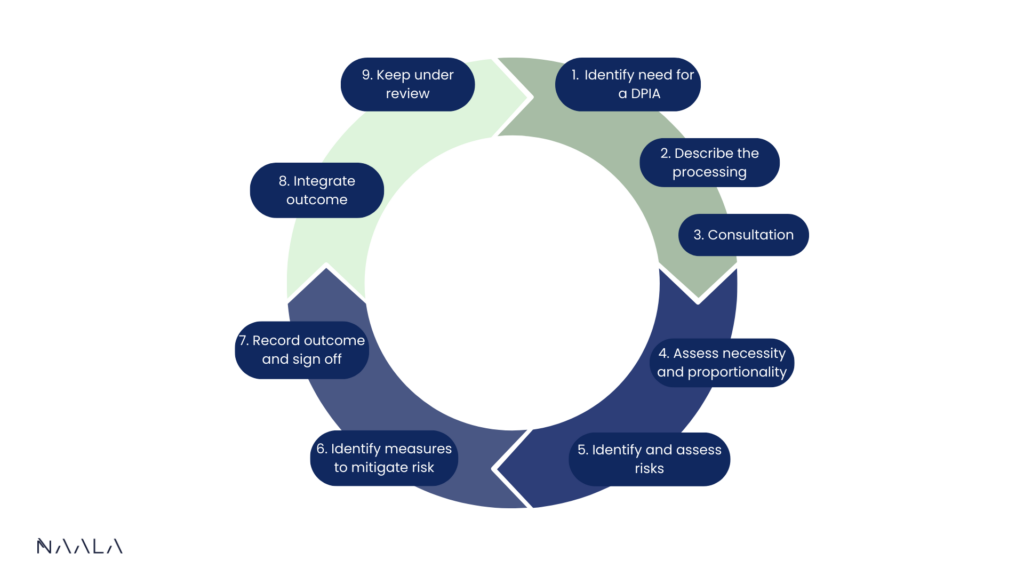
A DPIA needs to be performed before the data is going to be processed. Several steps must be completed during a DPIA:
The first step should obviously be to identify if a DPIA needs to be conducted. For example, if health data is going to be processed a DPIA must be carried out. Include in the DPIA why exactly it needs to be performed.
Secondly, the processing itself must be described. Consider what the processing will look like, what it entails and what is involved. For example, include how much data is involved, where the controller is located, etc.
The consultation step will require you to consult various stakeholders regarding the data that will be processed. For example, consult the opinions of individuals, indicating how and when they will be consulted. Also, specify whether individuals within the organization should be involved and whether assistance from other organizations is required.
Next, the necessity and proportionality of the data processing will have to be considered. For this you will need to answer questions such as what is the base for processing the data, can the purpose for which the data is being processed be achieved in another way, what information will be provided to individuals etc.
Risks will have to be identified next. Identify relatively important risks that may arise when the data is processed. An example of a risk is that the data may be inadequately secured or that data may be hacked.
When the risks have been identified they must be assessed. This involves considering the probability of occurrence and the severity of the damage if the risks arise. These two factors will then have to be balanced together to come up with the total risk.
In the last step, the risks were identified. In order to prevent these risks or to lower the remaining risk to a level that is acceptable, measures must be taken.
Consider what measures can be taken to mitigate the identified risks. Record in the DPIA which measures can be taken for the risk and what effect this will have on the risks. This will demonstrate that the measures actually contribute to mitigating the risks.
Finally, you will need to indicate what the final remaining risk will be when the measures are implemented.
All the steps described above must be documented. A convenient way to do this is to use an excel table. With the documented excel table, for example, it can be demonstrated that a DPIA has been carried out and what the outcomes are.
When the DPIA is fully executed, the document needs to be signed. This means that the person authorized to do so approves the drafted measures, remainder risks, consultations etc. In the DPIA carried out, record that these elements have been signed by the authorized person. Be aware that advice needs to be sought from the Data Protection Officer when a DPIA is conducted. In the end, he must agree with the DPIA conducted and the accompanying measures.
When the DPIA is carried out, a number of measures will be drawn up that will mitigate the identified risks. To ensure that this actually happens in practice, steps will have to be taken to implement the measures within the organization. It is therefore important to draw up a plan on how the measures and other outcomes of the DPIA will be implemented in the organization. In addition, it is necessary to see whether the steps that have to be taken are actually being carried out.
It is important to keep the DPIA under review. It is possible that aspects included in the DPIA change. These changes may lead to different outcomes, such as measures that no longer being effective. Therefore, appoint someone who will be responsible for maintaining and monitoring the DPIA. Include who that is in the DPIA as well.
- Continuity. A DPIA process can be viewed as a cycle. The steps that need to be performed are carried out in specific stages. In addition, the cycle continues; if something changes, you need to go through the steps again. To show what this cycle entails and how the steps relate to each other, the illustration below can be consulted.
Final
Now that you have delved into the fine details of DPIAs, you should have a clearer picture of what they entail, their crucial role in data protection and how to properly navigate this process yourself.
Hungry for more insights? Visit our Privacy Knowledge Center or reach out for a deeper conversation on this topic.
Questions? We are happy to discuss your specific case.
Related
Do you find yourself being responsible for more requirements than you anticipated due to the processing of personal data? As you may know, all data subjects (the natural persons you process data of) deserve protection of their information and have rights related to their data.
If you’re running a website or an app that collects personal data from your users, you need to pay attention to how you handle their information. In this guide, we’ll show you how to write a GDPR privacy statement that covers all the bases and boosts your credibility.
If you’re running a website or an app that collects personal data from your users, you need to pay attention to how you handle their information. In this guide, we’ll show you how to write a GDPR privacy statement that covers all the bases and boosts your credibility.
Please note that all details and listings do not claim to be complete, are without guarantee and are for information purposes only. Changes in legal or regulatory requirements may occur at short notice, which we cannot reflect on a daily basis.